Springs may appear simple, but their behavior and integrity when in use can change dramatically when exposed to extreme heat or extreme cold. Temperature plays a critical role in how a spring functions in any application. At Apex we have a deep understanding of materials and engineering around those challenges.
How Extreme Heat Affects Springs
At high temperatures, metallic springs can face several issues:
- Loss of Strength and Load Capacity
As temperature rises, the elastic modulus of common spring materials (like carbon steel or stainless steel) decreases, this reduces stiffness and, as a result, also reduces the force the spring can deliver. - Creep and Stress Relaxation
Under constant load, springs at high temperatures can slowly deform over time—a phenomenon known as creep. This deformation can permanently alter the spring’s free length, diminishing its capacity to return to its original shape. Additionally, stress relaxation can occur, meaning the spring gradually loses its ability to maintain load. - Fatigue Weakening
Repeated cycling under elevated heat accelerates fatigue. High temperatures can amplify microstructural changes, making it more likely for cracks, ultimately shortening the spring’s life. - Dimensional Instability
Over time, sustained high heat can cause permanent deformation, altering the spring’s set length or coil geometry—and ultimately its predictable behavior. - Oxidation and Corrosion
In hot environments, oxidation speeds up. For some materials, this can lead to surface degradation or pitting, which act as stress concentrators and make fatigue failure more likely.
Challenges at Very Low Temperatures
Cold conditions bring a different set of issues:
- Brittleness: Many metals lose ductility as temperature drops, making springs more prone to cracking or fracture under load.
- Reduced Deformation Capacity: At very low temperatures, the elastic behavior can be compromised—springs may not flex as intended and could fail under what would otherwise be safe loads.
- Thermal Shock: Rapid temperature changes (for example, from hot to cold) can produce thermal shock. Differential expansion or contraction within the spring can generate internal stresses, potentially causing cracks or permanent damage.
How Manufacturing Helps: Preparing Springs for Extremes
At Apex, manufacturing is about more than just shaping wire — it’s about engineering for reliability in the conditions your application demands to avoid spring failure.
- Material Selection
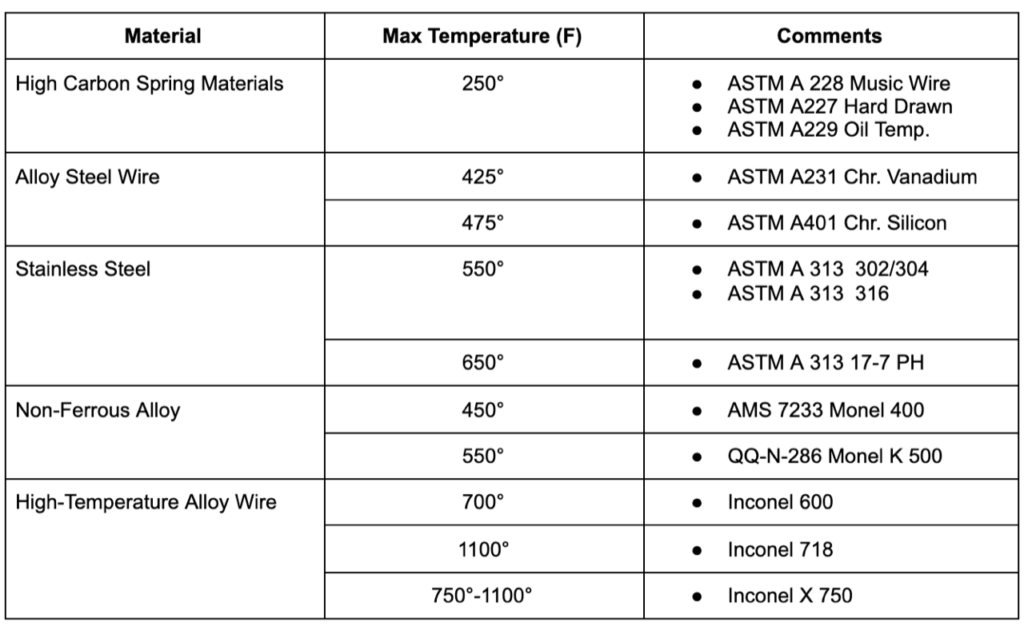
The first line of defense in extreme-temperature applications is choosing the right alloy. Nickel-based superalloys are good for high-heat environments thanks to their exceptional thermal stability, resistance to oxidation, and ability to retain strength at very high temperatures. On the cold side, materials are selected based on their ductility at low temperatures to avoid embrittlement. - Heat Treatment and Stress Relieving
After forming or coiling, springs undergo controlled heating and heat treatment. This process helps stabilize their internal structure by relieving residual stresses. For heat-critical springs, carefully calibrated aging or stress-relieving cycles can minimize future stress relaxation and creep. Apex’s expertise ensures we deliver springs that retain integrity even after high-temperature service. - Design Adjustments
Geometry matters. During design, parameters such as coil diameter, wire thickness, number of active coils, and free length are optimized to account for thermal expansion, load loss, and stress changes at operating temperature. For example, a thicker wire may better manage thermal gradients but also introduce more internal stress, so tradeoffs must be balanced. - Surface Treatments & Finishes
Protective coatings—like nickel plating, black oxide, or other specialized finishes—can significantly improve resistance to oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures. Additionally, techniques like shot peening can enhance fatigue life by introducing compressive surface stresses. Though at extreme temperatures, some of those benefits may diminish due to thermal relaxation; Apex calibrates these processes specifically for high-temperature performance. - Testing & Validation
It’s one thing to design for extreme conditions; it’s another to test in them. Apex supports thermal cycling, load testing, and fatigue simulation under conditions that mimic real-world use. These tests validate that springs will perform as expected, with stable force output and minimal dimensional change, even after exposure to thermal stress. - Presetting
For critical applications, springs can be pre-compressed (“preset”) beyond their working load during manufacturing. This process helps stabilize their behavior under later operating conditions, reducing the likelihood of sudden shifts in force due to relaxation or long-term creep.
Apex Can Help!
Temperature extremes in spring application can not be ignored in engineering and manufacturing. Therefore, at Apex we bring a deep understanding of how materials, heat treatment, and design come together to create springs that thrive in any environment.
Our engineering team can help you select and build springs that maintain precision, strength, and longevity no matter how hot or cold it gets. Contact us today, we can help!